Meta Description: Boost your WordPress site’s SEO with Nginx expire headers. Learn to configure caching for faster load times and better Core Web Vitals in this step-by-step guide.
Want to boost your WordPress site’s SEO? Configuring Nginx expire headers is a powerful way to improve page load times, a key factor in Google’s Core Web Vitals. By caching static assets like images, CSS, and JavaScript, you reduce server requests, enhance user experience, and improve metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP). This guide shows you how to set up expire headers for your WordPress site running on Nginx with PHP.
Why Nginx Expire Headers Improve SEO
Expire headers tell browsers to cache static files, reducing load times and server strain. Here’s why they matter for your site:
- Faster Page Loads: Caching reduces LCP, boosting SEO rankings.
- Lower Server Load: Fewer requests free up resources for dynamic WordPress content.
- Better User Experience: Faster pages lower bounce rates, signaling engagement to search engines.
- Mobile Optimization: Cached assets reduce data usage, improving mobile performance.
- PHP 8.3
- Nginx Certbot SSL enabled
- Ubuntu Server 24.04
Prerequisites
Before you start, ensure you have:
- A WordPress site at
/var/www/html/wordpresson server. - Nginx server with
root accessto edit configuration files. - PHP 8.3 with PHP-FPM configured.
- Certbot for SSL (already set up).
- A backup of your Nginx configuration.
Step-by-Step Guide to Configure Nginx Expire Headers
Follow these steps to add expire headers to your Nginx configuration safely, optimized for SEO and WordPress.
Step 1: Backup Your Nginx Configuration
Protect your live server by backing up your configuration:
sudo cp /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domain.com /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domain.com.bakStep 2: Edit the Nginx Configuration File
Open your site’s configuration file (likely /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domain.com):
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domain.comReplace its contents with this SEO-optimized configuration:
# HTTPS Server Block
server {
listen 443 ssl; # Managed by Certbot
listen [::]:443 ssl ipv6only=on; # Managed by Certbot
server_name your_domain.com www.your_domain.com;
root /var/www/html/wordpress;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
client_max_body_size 64M;
# SSL Configuration (Managed by Certbot)
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/fullchain.pem; # Managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/privkey.pem; # Managed by Certbot
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # Managed by Certbot
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # Managed by Certbot
# WordPress Rewrite Rules
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
# Expire Headers for Static Assets (SEO-focused)
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js|woff|woff2|ttf|svg|eot|pdf|webp)$ {
expires 90d; # Cache for 90 days
add_header Cache-Control “public, must-revalidate”; # Supports WordPress ?ver= query strings
add_header Vary “Accept-Encoding”; # Supports Gzip
access_log off; # Reduce server load
}
# PHP Processing
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php8.3-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
# Deny Access to Sensitive Files
location ~* /(wp-config\.php|readme\.html|license\.txt|xmlrpc\.php|\.ht) {
deny all;
}
# Gzip Compression for Performance
gzip on;
gzip_types text/css application/javascript image/svg+xml application/font-woff2;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_vary on;
# Security Headers for SEO and Protection
add_header X-Content-Type-Options “nosniff”;
add_header X-Frame-Options “DENY”;
add_header X-XSS-Protection “1; mode=block”;
}
# HTTP to HTTPS Redirect
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name your_domain.com www.your_domain.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri; # Redirect all HTTP to HTTPS
}Key Settings:
expires 90d:Caches static files for 90 days, balancing SEO and WordPress updates.Cache-Control: public, must-revalidate: Ensures compatibility with WordPress’s?ver=query strings.gzip: Compresses files for faster loading.access_log off: Reduces server load for static assets.- Security headers enhance trust signals for SEO.
Step 3: Test the Configuration
Verify syntax to avoid errors:
sudo nginx -tExpected output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf text is successfulIf errors occur, check for typos or incorrect paths (e.g., /var/run/php/php8.3-fpm.sock).
Step 4: Apply Changes Safely
Reload Nginx without downtime:
sudo systemctl reload nginxIf issues arise, revert to the backup:
sudo cp /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domain.com.bak /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domain.com
sudo systemctl reload nginxStep 5: Verify Expire Headers
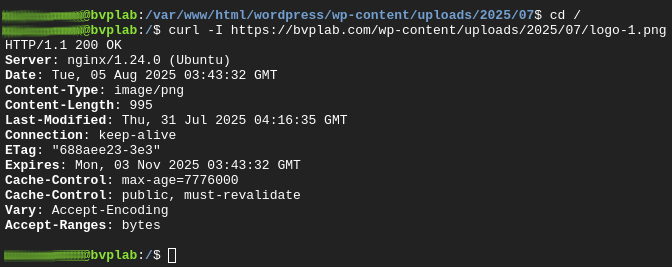
Test a static asset:
curl -I https://your_domain.com/wp-content/uploads/sample.jpgExpected output:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.24/0 (Ubuntu)
Date: Tue, 05 Aug 2025 03:43:32 GMT
Content-Type: image/png
Content-Length: 995
Last-Modified: Thu, 31 Jul 2025 03:43:32 GMT
Connectiong: keep-alive
ETag: “688aee23-3d3
Expires: Mon, 03 Nov 2025 03:43:32 GMT
Cache-Control: max-age=7776000
Cache-Control: public, must-revalidate
Vary: Accept-Encoding
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Check headers in browser DevTools (Network tab) for .jpg, .css, .js, etc.
Step 6: Test WordPress Functionality
- Visit
https://your_domain.com, sample posts, and/wp-admin. - Ensure updated CSS/JS files (with
?ver=) load correctly. - Confirm no 502/404 errors.
Additional SEO Tips for your_domain.com
- Shorter Expirations for CSS/JS: If you update themes/plugins often, use: Bash
location ~* \.(css|js)$ { expires 30d; add_header Cache-Control “public, must-revalidate”; } - Caching Plugins: Pair with WP Rocket or W3 Total Cache for dynamic caching.
- CDN: Use Cloudflare with “Respect Existing Headers” for global caching.
- WebP Images: The
locationblock includes.webpfor modern formats. Use plugins like ShortPixel for conversion.
Troubleshooting
- 502 Errors: Verify
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php8.3-fpm.sockmatches your PHP-FPM socket. - Stale Assets:
must-revalidateensures?ver=query strings work. - Logs: Check
/var/log/nginx/error.logor/var/log/php8.3-fpm.log. - Rank Math Conflicts: Ensure caching plugins don’t override Nginx headers.
Conclusion
Configuring Nginx expire headers on your_domain.com is a simple yet effective way to enhance WordPress SEO. By caching static assets, you’ll improve load times, Core Web Vitals, and user experience. Combined with Rank Math SEO, this setup can skyrocket your rankings.
Have questions or success stories? Share in the comments below!